

Whereas the treatment of significant hyperkalaemia is pre-emptive in the patient without electrocardiographic change, in the presence of electrocardiographic change significant hyperkalaemia represents a true medical emergency and requires rapid implementation of measures to reduce serum potassium concentration. Abstract Hyperkalemia is a common cause of electrolyte induced cardiac conduction disturbance. objective findings in a specific clinical context pertaining to emergency medicine and critical. Continuous ECG monitoring should occur until serum potassium values have been brought into a safe range and cardiotoxicity has resolved. Significant hyperkalaemia represents a medical emergency, and an ECG should be obtained to establish whether cardiotoxicity is present. Copyright ©2009 by the BMJ Publishing Group. As hyperkalemia worsens, the ECG first demonstrates peaked T waves resulting from global APD shortening causing more synchronous repolarization across the ventricular wall. : ECG changes in patients with hyperkalaemia BMJ 2009 339:b4114. Mattu A, Brady WJ, Robinson DA. Electrocardiographic manifestations of hyperkalemia. Clinical manifestations of hyperkalaemia are uncommon with values <6.0 mmol/L (<6.0 mEq/L).Ĭommon acute manifestations of significant hyperkalaemia include muscle weakness and ECG changes, with the latter having the potential to progress to a life-threatening arrhythmia. There is a limited correlation between an elevated serum potassium value and an excess in total body potassium stores. Hyperkalaemia is most commonly due either to high intake of potassium in the setting of decreased renal excretion or to extracellular redistribution of potassium from intracellular locations. Small changes in serum potassium values can have significant muscular and cardiac effects when significant hyperkalaemia is present. Media in category 'SVG ECG graphs of hyperkalemia' The following 2 files are in this category, out of 2 total. View Media Gallery See also Cant-Miss ECG Findings, Life-Threatening Conditions: Slideshow, a Critical Images slideshow, to help recognize the conditions shown in various tracings.
Hyperkalemia ecg findings wikimedia free#
Moderate hyperkalaemia is defined as serum potassium values in the 5.0 to 6.0 mmol/L (5.0 to 6.0 mEq/L) range. From Wikimedia Commons, the free media repository.
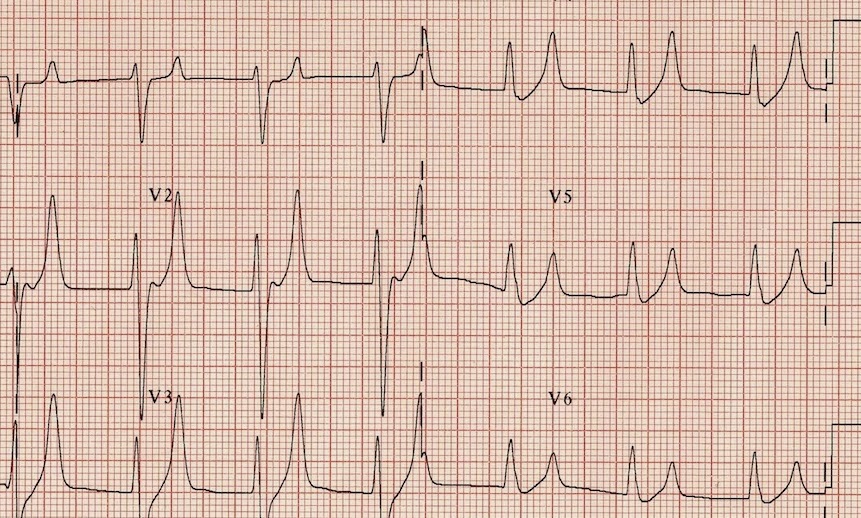
In this condition, as summarized by Figure 1, ECG changes, including expansive QRS complex, peaked T-wave, prolonged QT-interval, and hidden p-wave might be initiated 9-11. Significant hyperkalaemia is defined as a serum potassium value >6.0 mmol/L (>6.0 mEq/L). According to many studies, hyperkalemia strongly correlates with ECG manifestations.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
